Continuous Futures
Instructions
When adding futures market data to
When a futures contract expires (and if you have the feature enabled in Global Configuration), the system will automatically add the new lead month futures contract and removed the expired contract. When you use a Continuous Futures contract, it is no longer necessary to roll contracts, or to manually re-enter the new lead month if Automatic Rollover is disabled.”Additionally, it allows you to chart the future across multiple expiries, and apply moving averages and other technical studies that aren't relevant with the limited life of a single monthly or quarterly contract.
Enter a Continuous Futures Contract Using a Watchlist
-
Click in an empty row and enter the underlying symbol.
-
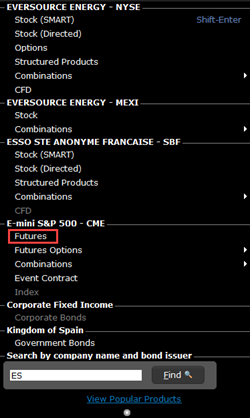
Hit enter, and select the futures contract from the list.
-
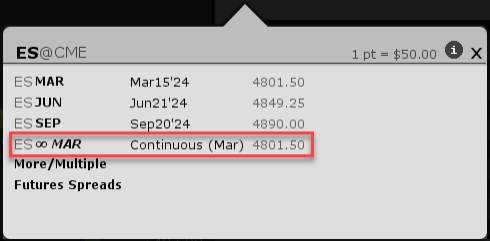
From the selector, choose the contract with the infinity sign (∞) which denotes a continuous futures contract.
-
The market data line for the future will also show the infinity sign.

See the Ratio Adjustment (RA) Points on a Chart
-
Open Global Configuration and select Charts on the left hand side.
-
Select Settings
-
Enable Show futures rollover points.
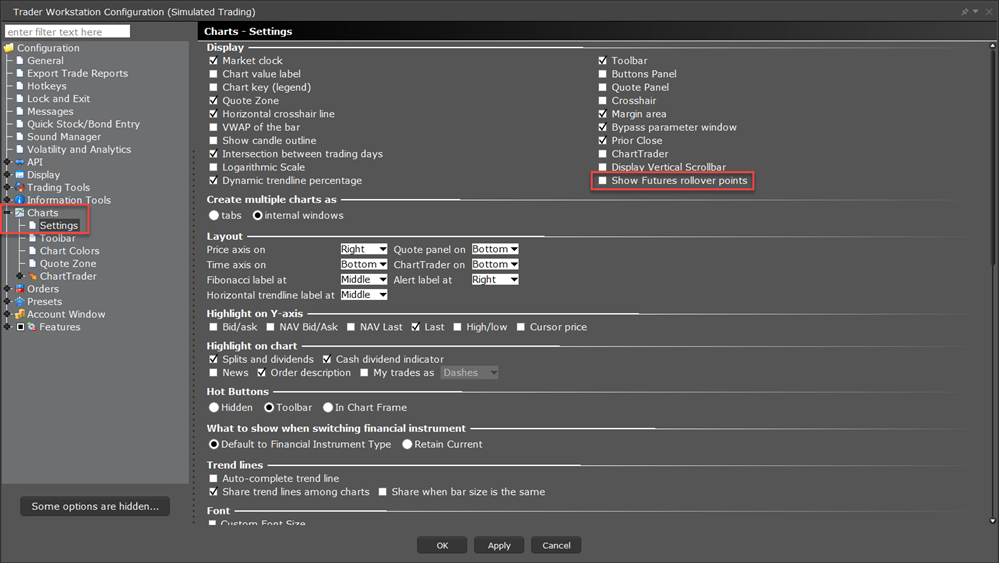
Note: These continuous contracts are for market data only; orders on futures are not updated. If you select a non-continuous contract, the Automatic Futures Rollover feature (if enabled) will notify you that the contract is expiring.
Generate Normalized Historical Data Series for Continuous Futures
A "continuous futures" contract represents a sequence of successively expiring lead futures contracts along with an associated interval during which each future is the lead. This allows us to construct a normalized historical data series for the contract. For example, we can construct a continuous futures contract for CL@NYMEX using the following contracts:
-
CL MAY'15
-
CL APR'15 20150317
-
CL MAR'15 20150217
-
CL FEB'15 20150115
-
CL JAN'15 20141216
-
CL DEC'14 20141117
-
CL NOV'14 20141016
-
CL OCT'14 20140917
-
CL SEP'14 20140817
-
CL AUG'14 20140717
-
CL JUL'14 20140617
-
CL JUN'14 20140515
-
CL MAY'14 20140417
The above list of sequential contracts shows the lead end dates when the particular contract stops being the lead contract and the next one takes over.
To generate a normalized historical data series for the above sequence, call CL MAY'15 as Contract A and CL APR'15 as Contract B. Then follow the steps below:
-
Take the closing price of Contract B and Contract A on 20150317.
-
Calculate the ratio of closingPrice(Contract A)/closingPrice(Contract B).
-
Multiply all Contract B data for 20150317 and all prior dates by this ratio. This results in the adjusted time series of Contract B having the SAME closing price on 20150317 as Contract A.
-
Repeat for prior months.